30 Dec 2025
Opening up new horizons in Niger
Our assets
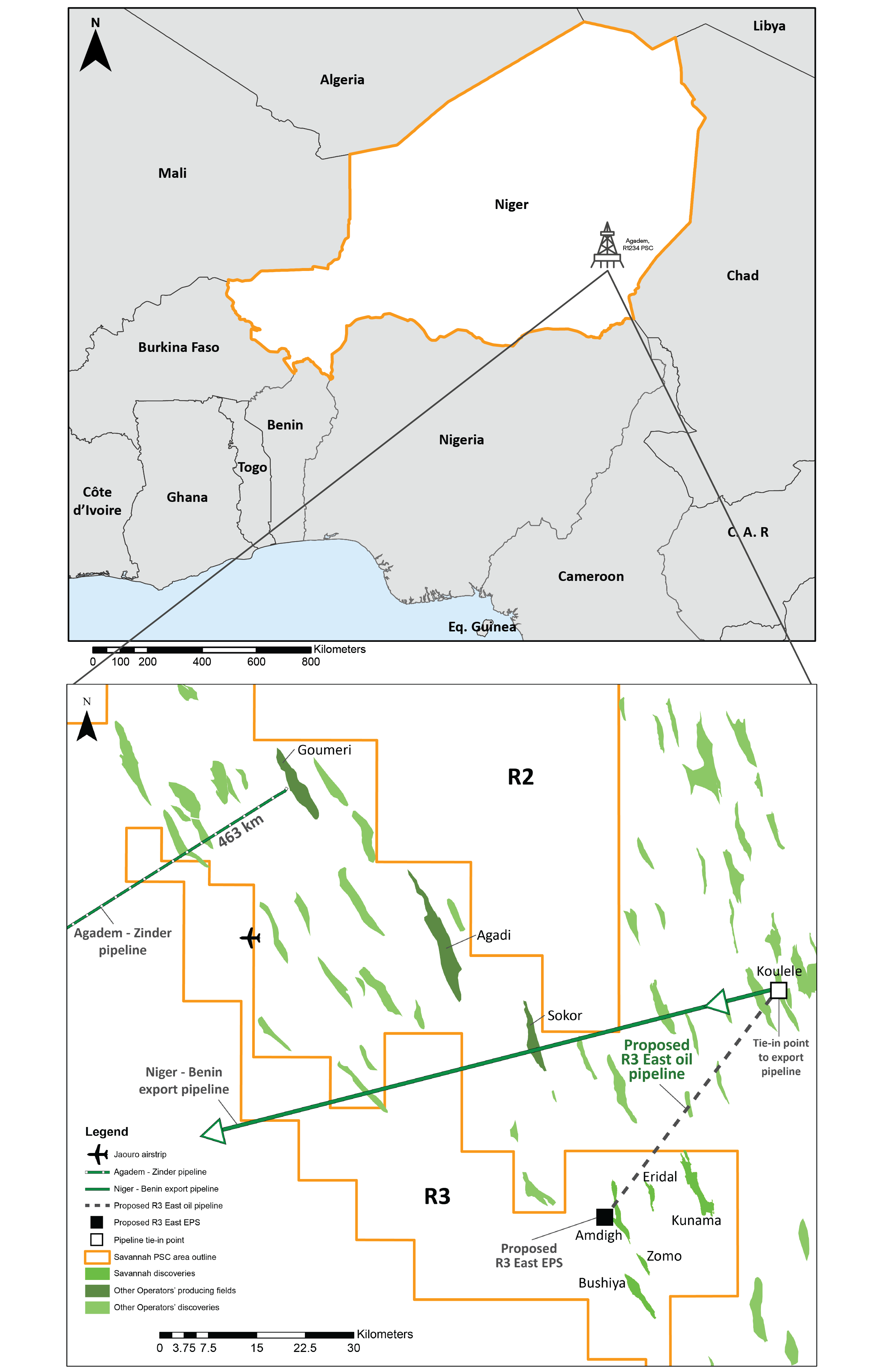
Hydrocarbon licence interests
Savannah’s hydrocarbon licence interests in the R1234 PSC area cover approximately 13,655 km2, equating to 50% of Niger’s main petroleum basin, the Agadem Rift Basin (“ARB”) in South East Niger.
35 MMstb
of Gross 2C Resources for our R3 East discoveries.
90 MMstb
of additional Gross Unrisked Prospective Resources (Best case) from five prospects and leads within tie-in distance to the planned R3 East facilities.
100% exploration success rate
achieved to date with five discoveries from five wells drilled.
146
potential exploration targets.

Our progress in the ARB
Savannah has delivered a highly successful exploration campaign in Niger with five discoveries from five wells in the R3 area. There are an additional five prospects and leads within tie-in distance to the planned R3 East facilities with three Yogou Cretaceous prospects mapped on 3D seismic, at depths below our main discoveries (i.e. Amdigh, Eridal and Bushiya), and two leads in the Central part of R3. Savannah has identified 146 potential exploration targets in total across our licence area to consider drilling in the future. The average geological chance of success for the Alternances exploration prospects and leads, such as those drilled to date by Savannah in the R3 East area, is estimated to be high, at more than 75%.1
Subject to a satisfactory agreement being reached with the Government, our subsidiary, Savannah Energy Niger SA, is considering commencing a four-well testing programme and/or a return to exploration activity in the R1234 PSC contract area in 2026/27. The Niger-Benin oil export pipeline, now fully operational, provides a potential route to international markets for crude oil produced from this area. The R3 East development plan has been significantly re-worked since the last published Niger CPR of December 20211, with a revised plateau production rate of around 10 Kbopd. Management estimates of the forecast PV10 value (on an unrisked basis) of the R3 East development also increased to US$184.4million (vs the last CPR asset value estimate of US$150 million). Assuming a successful well test programme is conducted, we would look to accelerate plans to commence commercial oil production from the R3 East Area.
Read more about the geology
of the ARB in our
latest Annual Report and Accounts
1. November 2021 Competent Persons Report by CGG Services (UK) Limited.



























